Deploying smart contracts
As an EVM-compatible chain, Etherlink runs Solidity contracts. You can deploy Solidity smart contracts in any way that you would deploy them to an EVM-compatible chain.
Etherlink supports Solidity versions up to and including 0.8.24.
You can use any of the toolkits in Development toolkits to deploy to Etherlink, as well as standard tools such as the Remix Ethereum IDE.
To call the contract after you deploy it, see Sending transactions.
Deploying with Remix
The Remix online IDE lets you code, compile, and deploy contracts to EVM chains, including Etherlink
-
Connect your wallet to Etherlink Shadownet Testnet as described in Using your wallet.
-
Get some Etherlink tokens as described in Getting Testnet tokens.
-
Open the Remix IDE at https://remix.ethereum.org.
-
In the contracts section of the IDE, create a contract. For example, you can create a contract named
4_HelloEtherlink.soland use this contract from the Solidity by Example:// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
// compiler version must be greater than or equal to 0.8.24 and less than 0.9.0
pragma solidity ^0.8.24;
contract HelloEtherlink {
string public greet = "Hello Etherlink!";
}The IDE looks like this, with your contract in the file explorer:
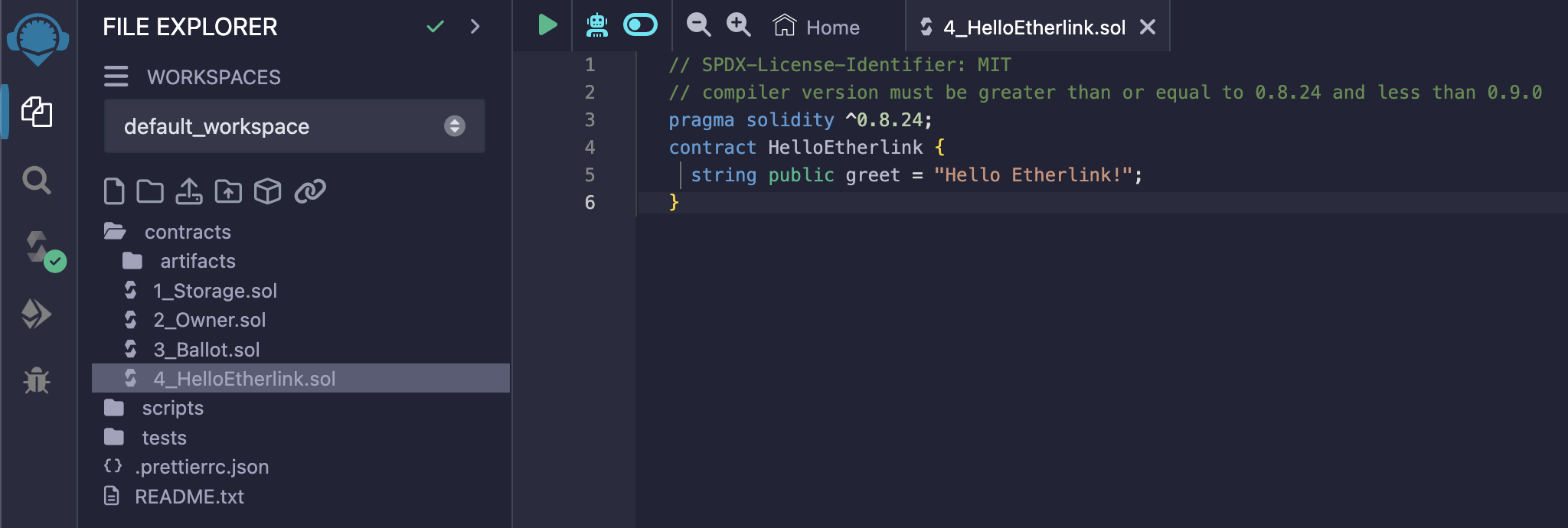
-
On the Compiler tab, select compiler version 0.8.24, as shown in this picture:
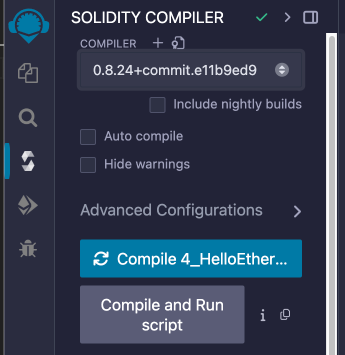
-
Compile the contract.
-
On the Deploy and Run Transactions tab, in the Environment list, select Browser extension > Injected Provider - MetaMask. Your MetaMask wallet opens to confirm the network connection.
-
In MetaMask, confirm the connection and select the account to use.
-
In the IDE, verify that the Account field shows your account and the tokens in it, as in this picture:
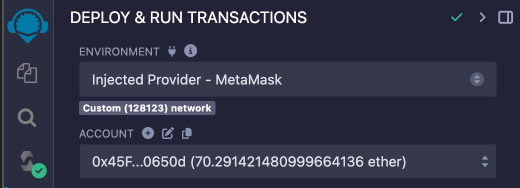
-
Click Deploy and confirm the transaction in MetaMask.
-
Call the contract by clicking the button for its entrypoint in the Deployed/Unpinned Contracts section. If you used the example contract above, you can call the
greetentrypoint and see the result underneath the button: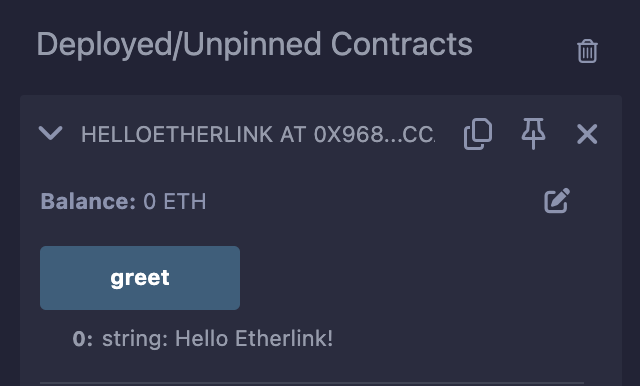
Now the contract is deployed on Etherlink. You can look it up on the Shadownet block explorer.
Deploying with ethers.js
If you have the compiled bytecode of the Solidity contract, you can use ethers.js to deploy it.
The following examples use the public Etherlink RPC endpoints listed in Network information, which are rate-limited. If you need to make requests in a production environment, run your own EVM node as described in Running an Etherlink EVM node and send the requests to it.
For example, this program uses ethers.js to deploy a contract:
const { ethers } = require("ethers");
const fullABI = []; // Add complete ABI here
const contractByteCode = "0x..."; // Add compiled bytecode here
// Define the provider by its RPC address
const provider = new ethers.JsonRpcProvider("https://node.shadownet.etherlink.com");
// Sender's private key
const privateKey = process.env.ETHERLINK_PRIVATE_KEY;
const wallet = new ethers.Wallet(privateKey, provider);
async function deployContract() {
// Create contract factory
const factory = new ethers.ContractFactory(fullABI, contractByteCode, wallet);
console.log("Deploying contract...");
const contract = await factory.deploy();
// Wait for deployment confirmation
await contract.deploymentTransaction().wait();
console.log("Contract deployed at:", contract.target);
}
deployContract();

 Page Outline
Page Outline